Using the NMDC API Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Note: This guide was written with respect to NMDC API version
2.13.0.
Retrieving metadata using "Metadata access" API endpoints
Metadata describing NMDC data (e.g. studies, biosamples, data objects, etc.) may be retrieved with GET requests, using the NMDC API Graphical User Interface (GUI). The API GUI provides a guided user interface for direct access to NMDC metadata. People can use it to:
- perform granular, targeted queries. This is especially helpful if a user has a query that may not be supported by the NMDC Data Portal yet.
- learn about querying capabilities. It provides code snippets that can be used in scripts for programmatic access, i.e. the request
curlcommands and URLs provided in the responses (please see the examples below).
The API endpoints are organized into five groups:
- Metadata access - Retrieve and manage metadata
- Workflow management - Manage workflows and their execution
- Persistent identifiers - Mint and manage persistent identifiers
- User accounts - Create and manage user accounts
- System administration - Retrieve system information
Please note that the endpoints discussed in this document were designed for use primarily by NMDC data consumers. For documentation describing other endpoints, primarily those designed for use by NMDC team members, please see the NMDC Runtime documentation.
API requests can include parameters to filter, sort, and organize the requested information. The Metadata access section contains endpoints using different query syntax approaches. Some endpoints use compact syntax (for example, filtering biosamples for those having an "Ecosystem Category" of "Plants" would involve submitting a request containing ecosystem_category:Plants to the GET /biosamples endpoint). Other endpoints use MongoDB-like query syntax (for example, the same filter would look like {"ecosystem_category": "Plants"} using the GET /nmdcschema/{collection_name} endpoint with collection_name set to biosample_set).
The following sections describe endpoints in the Metadata access groups.
Endpoints with compact syntax
The Metadata access section contains several endpoints that are dedicated to finding metadata of a specific type. There are endpoints specific to finding studies, others specific to finding biosamples, others for finding data objects, and still others for finding planned processes.
When preparing to submit an API request to one of these endpoints, we recommend reviewing the parameter options displayed in the endpoint's collapsible section on the API GUI.
Here are some of these endpoints that exist today:
 The
The GET /studiesendpoint is a general purpose way to retrieve NMDC studies based on parameters provided by the user. Studies can be filtered based on attributes of a Study, which are listed in the NMDC Schema documentation. If you already know the study's
If you already know the study's idvalue, you can get just that one study by using theGET /studies/{study_id}endpoint. The
The GET /biosamplesendpoint is a general purpose way to retrieve biosample metadata using user-provided filter criteria. You can filter based upon the applicable Biosample attributes. If you already know the biosample's
If you already know the biosample's idvalue, you can get just that one biosample by using theGET /biosamples/{sample_id}. To retrieve metadata about NMDC data objects (such as files, records, or omics data) the
To retrieve metadata about NMDC data objects (such as files, records, or omics data) the GET /data_objectsendpoint may be used along with various parameters. You can filter based upon the applicable Data Object attributes. If you already know the data object's
If you already know the data object's idvalue, you can get just that one data object metadata record by using theGET /data_objects/{data_object_id}endpoint.
For the latest, complete list of these endpoints, consult the "Metadata access" section of the API GUI.
Compact syntax endpoint example: Get all studies that have EMSL-related funding
Note: "EMSL" stands for "Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory".
- Click on the dropdown arrow to the right side of the
GET /studiesendpoint.
- Click Try it out in the upper right of the expanded endpoint box.

- Enter the query parameters. In this case, we will enter "
funding_sources.search:EMSL" into the filter parameter. The ".search" part tells the API you want it to perform a full-text search offunding_sourcesvalues, to find studies whosefunding_sourcesvalues have the word "EMSL" in them. - Click Execute.
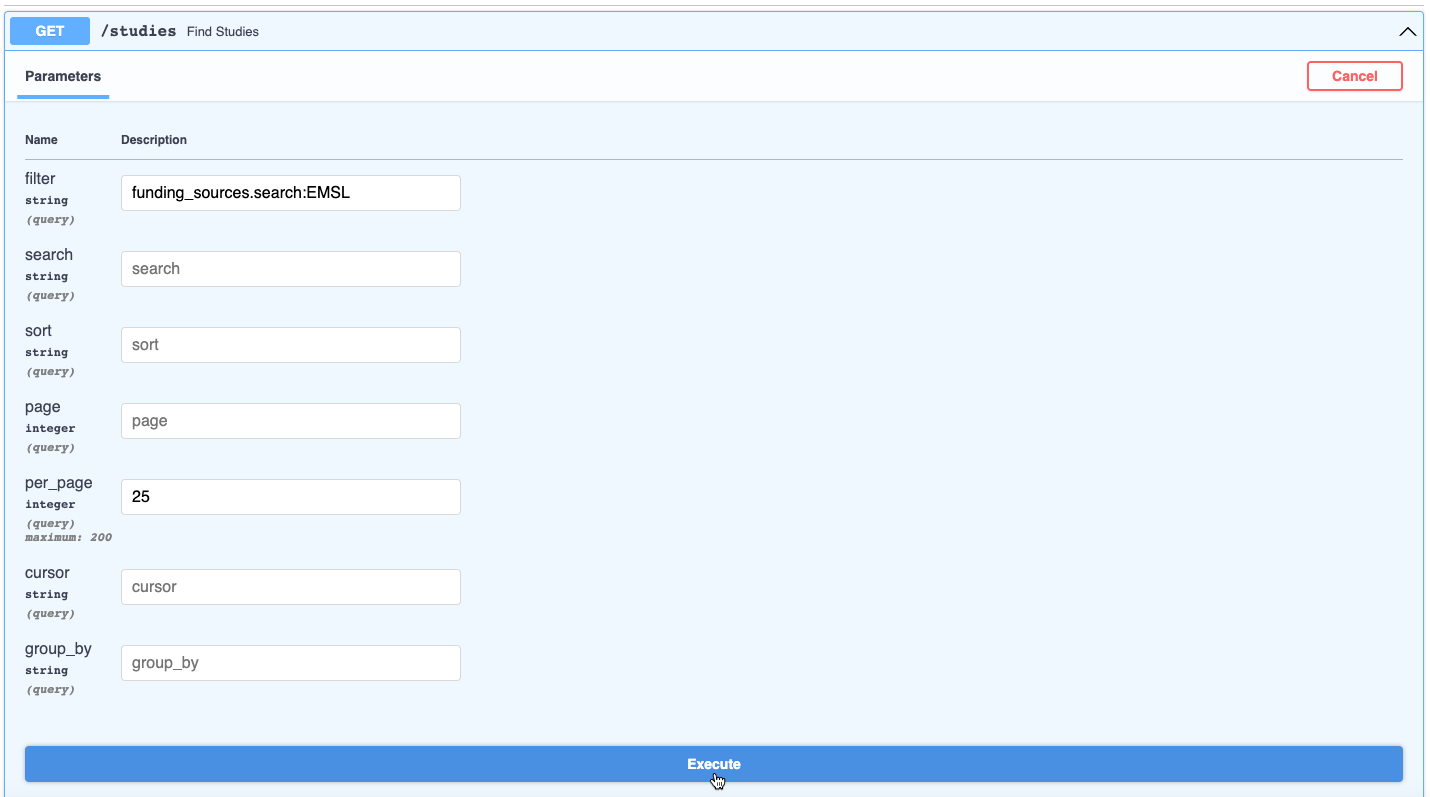
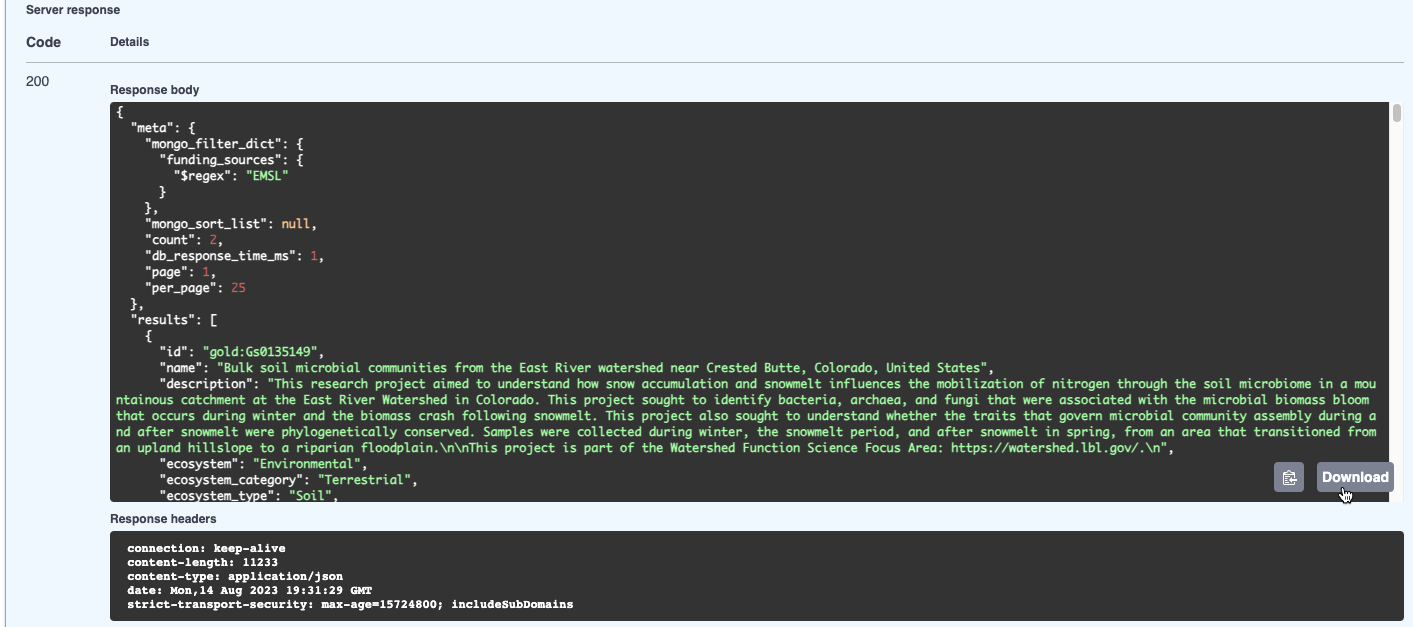
- View the API response body in JSON format. You can download it by clicking the Download button at the lower right, or copy the results by clicking the clipboard icon next to it. In this case, two studies were retrieved.
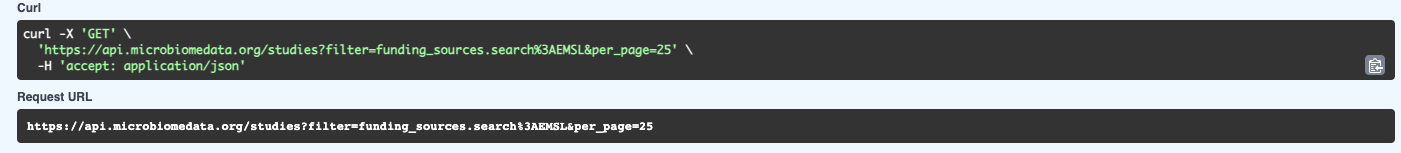
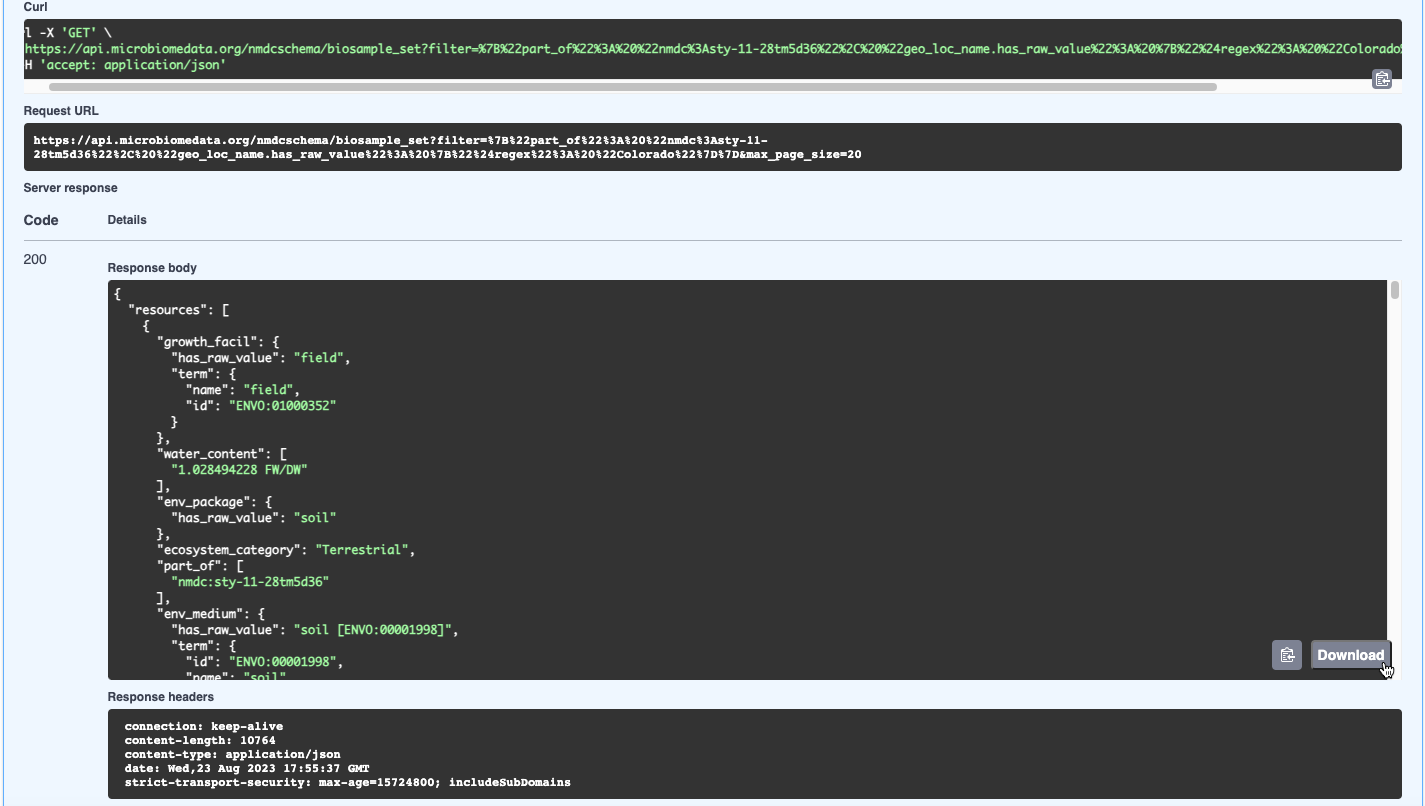
Note that an equivalent curl command and request URL are provided as well—complete with the request parameters—in case you want to perform the same request from a command line or script:
Endpoints with MongoDB-like query syntax
These endpoints can be used to get and filter metadata from collections (e.g. studies—which are in the study_set collection; biosamples—which are in the biosample_set collection; and data objects—which are in the data_object_set collection).
Unlike the compact syntax described above, the syntax for the filter parameter of these endpoints uses a MongoDB-like query syntax.
When preparing to submit an API request to one of these endpoints, we recommend reviewing the parameter options displayed in the endpoint's collapsible section on the API GUI.
Here are some of these endpoints that exist today:
 The
The GET /nmdcschema/{collection_name}endpoint is a general purpose way to retrieve NMDC metadata from a specific collection, given user-provided filter and projection criteria. Please see the Collection Names that may be retrieved. Please note that metadata may only be retrieved about one collection at a time. If you already know the
If you already know the idvalue of the metadata record (i.e. document) you want to retrieve, you can use theGET /nmdcschema/ids/{doc_id}to retrieve that record. If both the identifier and the collection name of the desired record is known, the
If both the identifier and the collection name of the desired record is known, the GET /nmdcschema/{collection_name}/{doc_id}can be used to retrieve the record. The projection parameter is optionally available for this endpoint to retrieve only specific attributes from a record (e.g. to get only the name of a study, rather than the entire study).
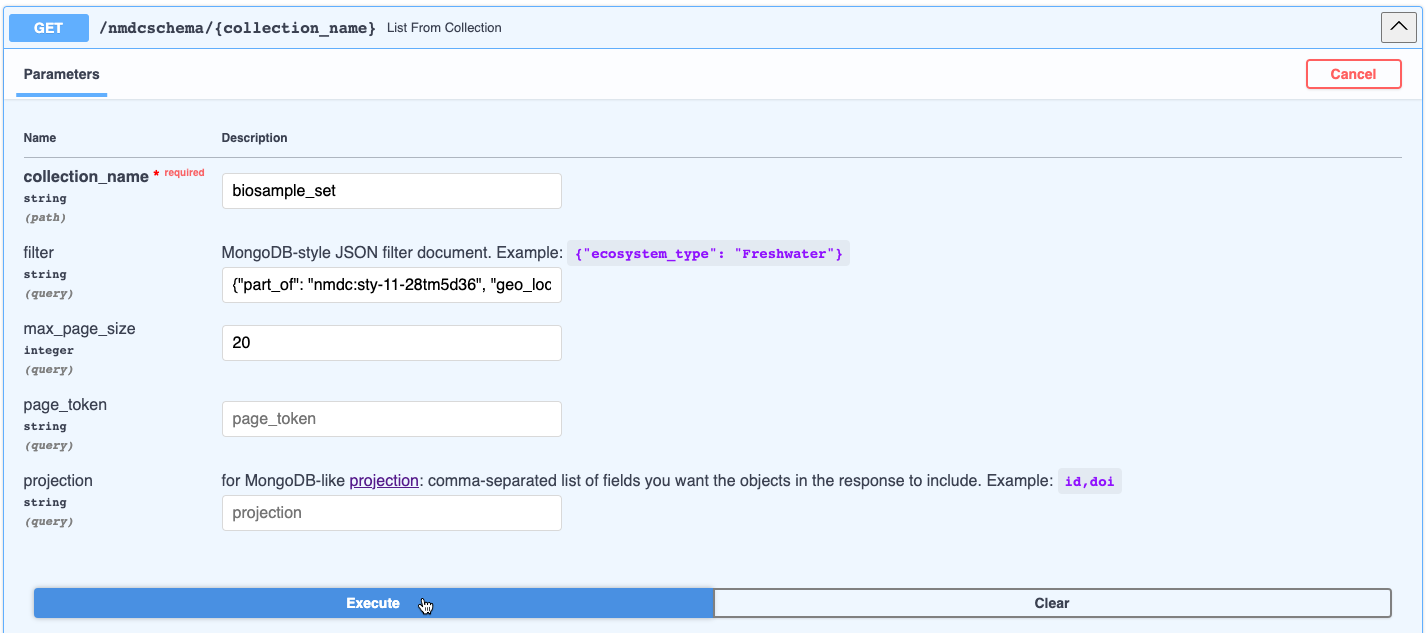
MongoDB-like query syntax endpoint example: Get all the biosamples that are part of the "1000 Soils Research Campaign" study sampled from Colorado
- Click on the dropdown arrow to the right side of the
GET /nmdcschema/{collection_name}endpoint.
- Click Try it out in the upper right of the expanded endpoint box.

- In order to enter the parameters, get the identifier for this study by navigating to the 1000 Soils Research Campaign study page in the NMDC Data Portal and copying the study's
IDvalue.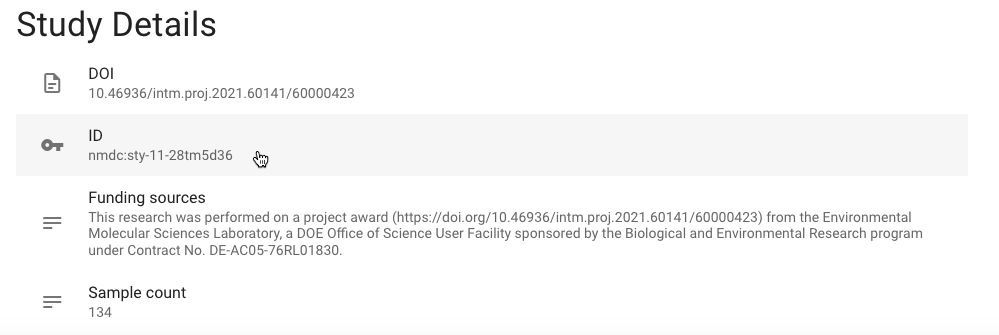
- Enter the parameters in the
GET /nmdcschema/{collection_name}endpoint. For this example, we will inputbiosample_setinto the collection_name parameter and{"part_of": "nmdc:sty-11-28tm5d36", "geo_loc_name.has_raw_value": {"$regex": "Colorado"}}into the filter parameter. See the Biosample Class in the NMDC Schema to view the applicable biosample attributes (slots); for this example, they arepart_ofandgeo_loc_name.has_raw_value. Note that$regexconducts a full text search for the word "Colorado" in thegeo_loc_name.has_raw_valueattribute. - Click Execute.
- View the results in JSON format, available to download by clicking Download; or copy the results by clicking the clipboard icon in the bottom right corner of the response. In this case, two studies were retrieved. Note that the curl and request URL are provided as well.
Retrieving metadata using a "Private" API endpoint
"Public" versus "Private" API endpoints
The previous section was about some API endpoints that people could access without being logged into the NMDC API GUI. People sometimes refer to endpoints like that as "public" API endpoints.
In contrast, this next section will be about API endpoints that people can only access when they are logged into the NMDC API GUI. People sometimes refer to API endpoints like these as "private" API endpoints.
We'll be using those terms—"public" and "private"—that way, in this section.
Logging into the NMDC API GUI
Here's how you can log into the NMDC API GUI:
- Visit the NMDC API GUI in your web browser if you aren't already there.
Notice that the padlock icon on the "Authorize" button is open, which signifies that you aren't currently logged into the NMDC API.
- Near the top of the page (above the endpoint sections), click the "Authorize" button.
A modal dialog will appear with available authorization options.
- In the authorization modal, scroll down and click the "Login with ORCID" link.
The "Sign in to ORCID" page will appear in a new window or tab.
- On the "Sign in to ORCID" page, enter and submit your ORCID credentials.
After successful authentication, the window will close and you'll return to the API GUI. The padlock icon on the "Authorize" button will be closed, signifying that you are logged into the NMDC API.
At this point, you are logged into the NMDC API GUI.
Accessing a "private" API endpoint
Now that you are logged into the NMDC API GUI, you can use the NMDC API GUI to access "private" API endpoints.
Here's how you can access a "private" API endpoint:
- Visit the NMDC API GUI in your web browser if you aren't already there.
- Confirm the "Authorize" button has a closed padlock icon on it, indicating that you are logged in.
- Scroll down to the Metadata access group of API endpoints.
- Click the
POST /queries:runsection (which has a padlock icon next to it) to expand it. - Click the "Try it out" button next to the "Parameters" heading.
- Populate the "Request body" field with the following JSON snippet:
json { "find": "study_set", "filter": {"ecosystem_category": "Aquatic"} } - Click the "Execute" button.
The NMDC API GUI will send an HTTP request to the NMDC API and display the response from the NMDC API.
Notice that the "Curl" command includes an
Authorizationheader that contains your access token. If you were making the API request via your command line instead of via the NMDC API GUI, you could include that same header in order to access "private" API endpoints. - View the API response body in the "Response body" section.
The API response body is a JSON object having several properties, including
okandcursor. Thecursorproperty contains an object having afirstBatchproperty, which contains the array of results that met the filter criteria that was specified in the API request. In this case, it contains all studies having anecosystem_categoryvalue of "Aquatic".